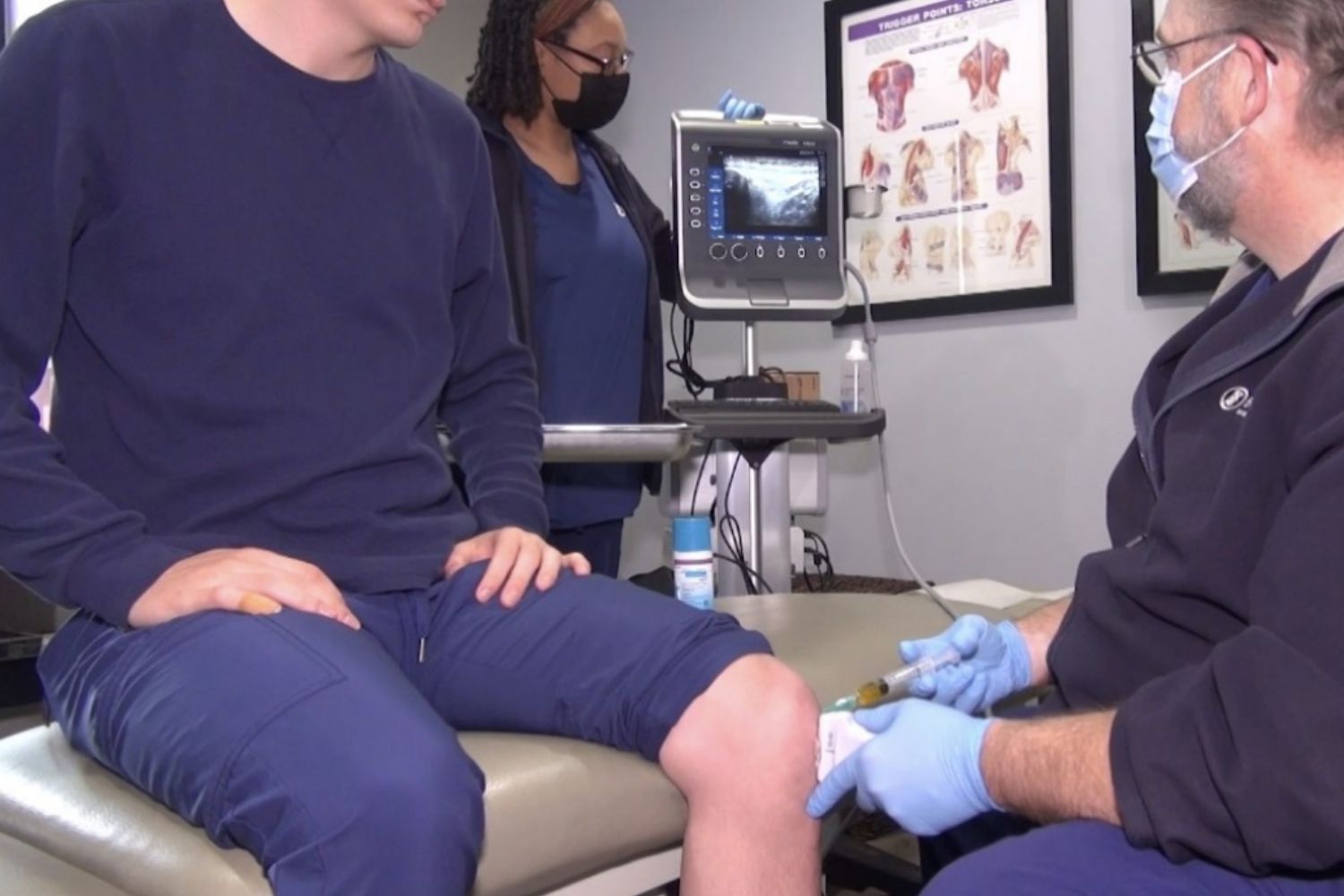
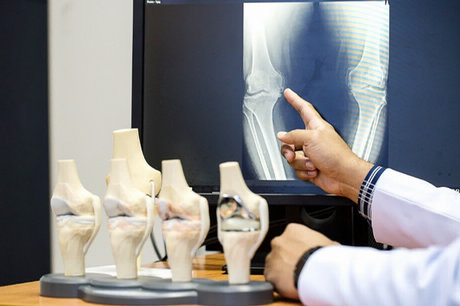
Traditional medical treatment for joint pain usually begins with addressing the inflammation, often with NSAIDs. This is generally effective for short term relief. If the pain continues, eventually x-rays and/or MRI imaging help develop a diagnosis.
Physical therapy is often needed after an injury or surgery. However, if all the potential causes of the joint pain are not addressed, the symptoms will likely continue to worsen over time.
Depending on the severity of the injury or condition, sometimes orthopedic surgery is unavoidable. Surgery should be a last resort whenever possible as the residual scar tissue is not nearly as flexible, functional, or strong as normal tissue. Scar tissue limits the mobility in a joint and that lack of movement is often the seed for degeneration of the joint.